The Aravalli Range is one of the oldest mountain ranges in the world, stretching approximately 800 kilometers across western India, from Gujarat through Rajasthan to Haryana and Delhi. Though often overlooked due to its low height compared to the Himalayas, the Aravallis play a critical role in India’s ecology, climate, water security, and biodiversity. Their protection is essential for sustainable development and environmental balance.
1. Natural Barrier Against Desertification
One of the most important roles of the Aravalli Range is acting as a natural barrier against the expansion of the Thar Desert. The hills slow down desert winds and help prevent sand from advancing eastward into fertile plains. Without the Aravallis, large parts of Haryana, Delhi, and western Uttar Pradesh would face increased desertification.
2. Climate Regulation and Rainfall Support
The Aravalli Range significantly influences the regional climate. It helps in:
- Deflecting monsoon winds, aiding rainfall in northwestern India
- Moderating extreme temperatures in nearby regions
- Reducing the impact of dust storms
This makes the Aravallis vital for maintaining a habitable climate in arid and semi-arid regions.
3. Water Conservation and Groundwater Recharge
The hills act as natural water catchments, helping store rainwater and recharge groundwater. Rivers such as Banas, Luni, and Sabarmati originate from the Aravalli Range. In regions where water scarcity is common, the Aravallis function as a lifeline by supporting aquifers, lakes, and wetlands.
4. Rich Biodiversity Hotspot
Despite their dry appearance, the Aravalli Range supports a wide variety of flora and fauna, including:
- Leopards, hyenas, jackals, and nilgai
- Indigenous trees like dhok, babool, and neem
- Numerous medicinal plants and bird species
Protected areas such as Sariska Tiger Reserve and Mount Abu Wildlife Sanctuary are part of the Aravallis, highlighting their ecological value.
5. Livelihood Support for Local Communities
Millions of people depend on the Aravalli ecosystem for:
- Agriculture and grazing
- Forest produce
- Eco-tourism and handicrafts
Sustainable use of the Aravallis ensures long-term economic security for local communities, especially tribal populations.
6. Cultural and Historical Significance
The Aravalli Range has witnessed centuries of Indian history. Ancient forts, temples, and cities like Udaipur, Mount Abu, and Alwar are closely tied to these hills. The range has protected civilizations and shaped settlement patterns for thousands of years.
7. Protection Against Environmental Disasters
The Aravallis help prevent:
- Soil erosion
- Flooding during heavy rainfall
- Air pollution by acting as a green lung near urban centers like Delhi-NCR
Their forests absorb carbon dioxide and improve air quality, making them crucial in the fight against climate change.
8. Threats to the Aravalli Range
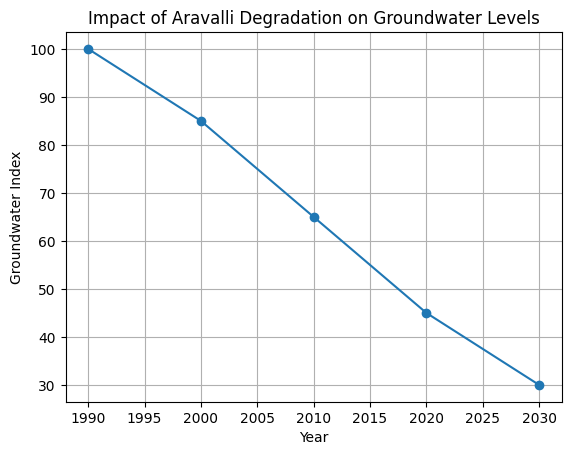
Despite their importance, the Aravalli Range faces severe threats:
- Illegal mining
- Deforestation
- Urbanization and infrastructure development
These activities have weakened the range, leading to water shortages, biodiversity loss, and rising temperatures.
9. Need for Conservation and Sustainable Development
Protecting the Aravalli Range requires:
- Strict enforcement of environmental laws
- Restoration of degraded forest areas
- Promotion of eco-friendly tourism
- Public awareness and community participation
Conservation is not a choice but a necessity for India’s environmental future.
Conclusion
The Aravalli Range is more than just an ancient geological formation—it is a shield against desertification, a source of water, a climate regulator, and a biodiversity haven. Preserving the Aravallis is crucial for ensuring ecological balance, water security, and sustainable living for future generations. Protecting the Aravallis today means safeguarding India’s tomorrow.



